
This approach allows for flexibility in handling different data types as keys and enables.
For instance the second element of the list which belongs to the key (1,2,3). By using the elements as keys and their counts as values in the dictionary, we can efficiently keep track of unique values. I have a dictionary of tuples as keys and lists as valued called dictionary as shown below from which I only wanna change the values of the elements in the list that are 67. This function takes in the list of dictionaries. As such, it can be indexed, sliced, and changed. An alternative method to count unique values in a list is by utilizing a dictionary in Python. To sort a list of dictionaries by a value of the dictionary in Python, you can use the sorted() function.
#Python list of dictionaries change value how to
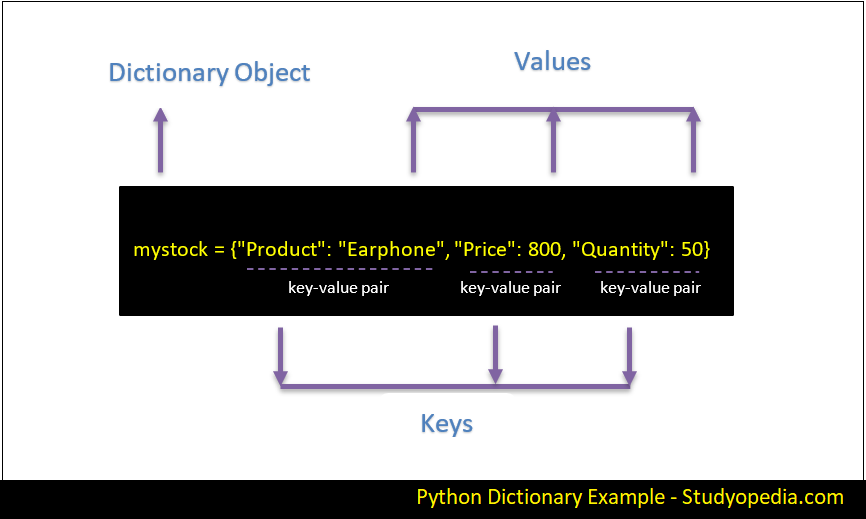
A list is a mutable, ordered sequence of items. I am looking for some help in understanding how to ask Python to go for the next line instead of using the same line from the code below. While we're at it, it may be helpful to think of them as daily to-do lists and ordinary school dictionaries, respectively. Key function: def getname (d): ''' Return the value of a key in a dictionary. A dictionary is a collection of key: value Dictionary in Python. enumerate() will return an enumerate object. We can change or modify the items in list, but cannot change or modify the values stored.
#Python list of dictionaries change value update
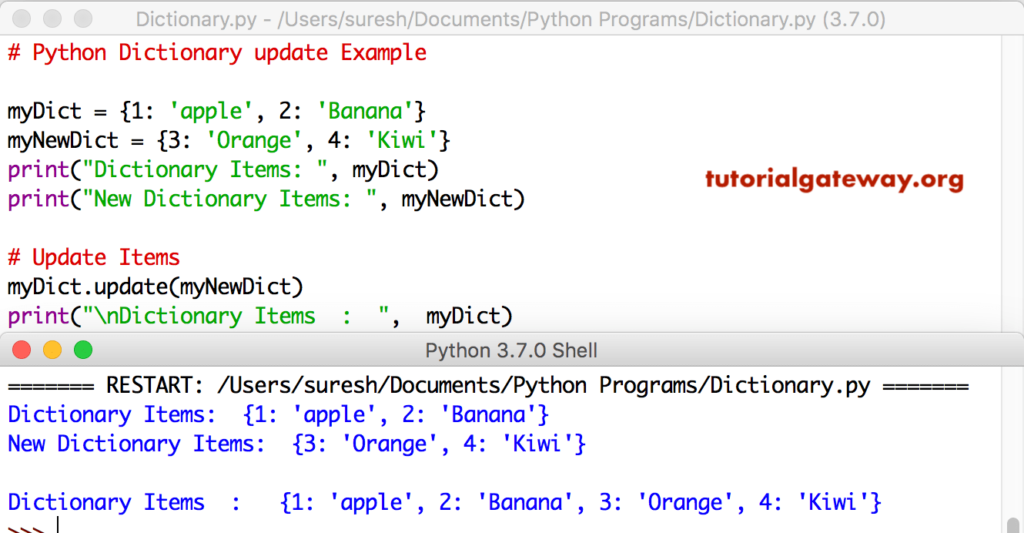
I want to update the value of a particular key in the list of dictionaries.įor example I have the following list of dictionaries (Input values): deviceDynamics = īut it is not changing the other created keys value. Introduction Before we dive into our discussion about lists and dictionaries in Python, we’ll define both data structures. If you do not need the original list of dictionaries, you could modify it in-place with sort () method using a custom key function. By using enumerate(), we can convert a list into a dictionary with index as key and list item as the value.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
